I started this site to get practice in writing science for the general populace. I've slacked off because I am a bit bored of reaching for topics. More importantly, I've been playing rugby with HBSRFC.
So here it is. A generalized and very incomplete version of my view on climate change, who it will affect most, and what we can do about it.
CO2, The Ugly One That Won't Leave You Alone
CO2 stays in the environment for more than 40,000 years. That is longer than nuclear waste lasts. Moreover, its effects are experiences by every person on the planet. What we do now has an effect on the entire planet. Luckily, technology will probably be able to fix this eventually. We can't count on this now, though.
Energy and Climate Change, How They Relate
Climate change is caused by emissions of CO2 by energy use, methane by agriculture and other things, and a host of other very powerful chemicals that are emitted from industry.
How do we solve climate change? The answer is straightforward, but far from simple: use much less energy from sources that produce CO2. Either switch to "green" tech, or conserve. Buy less things that require all the energy to produce. Travel less, or travel in ways that produce less greenhouse gases. Make fewer babies. None of these are easily accomplished, unless you are poor and can't afford any of them. Even then, everyone is striving for a wealthier, more CO2-heavy lifestyle.
So let's assume for a second that people aren't going to change their lifestyles and conserve. We need ways to get energy without belching CO2 everywhere.
Live in Smaller Houses, Buy Less Stuff
You can't convince Americans to live in houses that are the size that Europeans live in and you can't convince them to give up their cars to take public transportation and live in cities (at least in the short term). Houses require energy to heat and cool. Smaller houses mean fewer drafts, leading to less heating and cooling needs.
How about green energy? We have reviewed those technologies. There isn't enough wind to provide sufficient wind power, and the wind isn't always blowing, so sometimes we won't have power when we want it. Hydro power is pretty much fully tapped. Tidal power is a joke in the big scheme. Solar could be an option, but it is currently far too expensive. It is not "deployable" in that with solar, you only get what the sun decides, so we will always need some backup power that can be turned on when we want. Solar doesn't work well at night, for instance. Moreover, the best places for solar are far from cities, so figuring out how to get the electricity from the countryside to the cities is a monumental task, especially in the US (even with eminent domain, getting the land to be the transmission lines through several states would be nearly impossible). So here we stand with three good reasons that solar won't solve our problem in the near future, and with the other resources insufficient. Pretty much, even if we do use solar to solve a lot of our problems, we still need some other energy source to provide baseline power.

Too small! Turn back!
What about buying less stuff? The amount of CO2 that goes into making cars, laptops, etc., is pretty big. How much stuff do you buy that you never use afterwards? Or you maybe use once a year or two? All of that, you could have rented, saved money, and saved space. Even better? The things that go into making electronics like cellphones are not easy to pull out of the ground. Tantalum in your cell phone is pretty much produced by indentured servitude in Africa. The other stuff that goes into electronics, the rare earth metals, these are not so rare. It just turns out that it is difficult to produce it without destroying the environment. The US has plenty of rare earth's the reason it is done in China is that they don't mind wrecking the environment and their workers (see bottom of that post). Yeah, we need electronics to communicate and keep things moving. We don't need a new iphone every 6 months. Those things last at least 2 years.
Energy for Transportation
This is a much larger hurtle. 35% of US energy consumption is in transportation. Transportation requires that the energy source be within the vehicle (unless you are in South Korea, where the energy source is induction and is beneath the road. Pretty badass, if you ask me). Batteries currently weigh a lot, don't have nearly as much energy per pound as gasoline, and require a long time to charge. The problem is not as bleak as it seems, however. Most driving in the US could easily be done with all-electric cars.

Your bus is ugly, but it charges while driving without producing its own CO2. Well done, South Korea.
Cars
I've also written about Electric Cars.
This is an area with a lot of potential. 120 million Americans commute to work by car. The average person lives fewer than 20 miles from work. Substantially all of them commute alone. The Nissan Leaf gets 75 miles before it needs to be recharged. The Tesla model S goes about 275 miles. No matter what the source of energy for an electric car, it produces less CO2 than a normal car. Going by the numbers available on these cars, we see that with the standard US energy mix (some renewables, lots of nuclear, a whole lot of natural gas), they produce between 33% and 50% the CO2 as a combustion engine.
Bicycles
I've written about bicycling. It's good for you, and saves the environment. Unless you eat only beef. Then you have other problems.
Power Generation: What Works
Wind power makes sense everywhere that there is a lot of wind, as long as it is onshore. Wind is pretty much going up everywhere that makes sense. It costs less than a new coal power plant, and is far cleaner.
Solar power is expensive. Is there anywhere it works well? Sure, just take a look at the electricity rates paid by different types of consumers. Commercial real-estate (stores, offices) and residential places (our homes) pay a huge premium on electricity. In most states, residents and commercial consumers pay nearly 15 cents per kwh, while industrial consumers pay closer to 7 center for a kwh. How does this stack up to costs to produce? Let's return to my favorite chart:
Table 1. Estimated levelized cost of new generation resources, 2018
|
|
U.S. average levelized costs (2011 $/megawatthour) for plants entering service in 2018 |
| Plant type |
Capacity factor (%) |
Levelized capital cost |
Fixed O&M |
Variable O&M (including fuel) |
Transmission investment |
Total system levelized cost |
| Dispatchable Technologies |
| Conventional Coal |
85 |
65.7 |
4.1 |
29.2 |
1.2 |
100.1 |
| Advanced Coal |
85 |
84.4 |
6.8 |
30.7 |
1.2 |
123.0 |
| Advanced Coal with CCS |
85 |
88.4 |
8.8 |
37.2 |
1.2 |
135.5 |
| Natural Gas-fired |
| Conventional Combined Cycle |
87 |
15.8 |
1.7 |
48.4 |
1.2 |
67.1 |
| Advanced Combined Cycle |
87 |
17.4 |
2.0 |
45.0 |
1.2 |
65.6 |
| Advanced CC with CCS |
87 |
34.0 |
4.1 |
54.1 |
1.2 |
93.4 |
| Conventional Combustion Turbine |
30 |
44.2 |
2.7 |
80.0 |
3.4 |
130.3 |
| Advanced Combustion Turbine |
30 |
30.4 |
2.6 |
68.2 |
3.4 |
104.6 |
| Advanced Nuclear |
90 |
83.4 |
11.6 |
12.3 |
1.1 |
108.4 |
| Geothermal |
92 |
76.2 |
12.0 |
0.0 |
1.4 |
89.6 |
| Biomass |
83 |
53.2 |
14.3 |
42.3 |
1.2 |
111.0 |
| Non-Dispatchable Technologies |
| Wind |
34 |
70.3 |
13.1 |
0.0 |
3.2 |
86.6 |
| Wind-Offshore |
37 |
193.4 |
22.4 |
0.0 |
5.7 |
221.5 |
| Solar PV1 |
25 |
130.4 |
9.9 |
0.0 |
4.0 |
144.3 |
| Solar Thermal |
20 |
214.2 |
41.4 |
0.0 |
5.9 |
261.5 |
| Hydro2 |
52 |
78.1 |
4.1 |
6.1 |
2.0 |
90.3 |
| |
Solar PV costs less in sunny areas than buying from the grid, as long as you are residential or commercial. A big industrial complex gets really cheap power, so they will never use something as expensive as PV.
The Future of Solar
Even if solar power is widely deployed in the future, it doesn't work at night. A lot of people in Houston, and other places that are unlivable without modern tech, would be unhappy if they couldn't sleep in AC. We don't have massive-scale battery tech to compensate, so we will still need baseload.
Baseload Power
There are two viable places to get baseload power. The first is nuclear power. The second is burning fossil fuels and then catching their CO2 and putting it underground.
Carbon Capture and Storage
This is a very unproven technology. We don't know if we can hold the CO2 underground forever (which is what would be necessary) or whether we can find a place for it. And there are only a few test cases for it. The numbers above are completely unreliable in terms of cost. This might be better in the future, but I would guess that it isn't viable for at least 15 years.
Another issue? You can't just start capturing CO2 emissions from any old power plant. Retrofitting the plant is expensive or impossible. Power plants are built to last 50 years. Even when we figure out carbon capture and storage, we can't easily retrofit old plants to make them work well.
Baseload?
So we need baseload. There are no green baseload sources. Making coal based powerplants green is not currently viable. Nuclear power doesn't produce much CO2, but it has nuclear waste. Nuclear waste lasts a long time. But it is the only power source that contains all its waste. It's manageable. And it decays faster than the Earth will take down CO2.

nuclear power plants are my favorite
What's the biggest problem with nuclear? I'll describe this in more detail later. The long version: it can't get financed. Short version: people are afraid of Nuclear. Cause three powerplants have blown up. Fukushima was completely preventable. The US literally told Japan twice to get their house in order, cause there was trouble.The USGS warned that the walls of Fukushima were not high enough to prevent tsunami flooding years ago. Had they followed through with the USGS recommendations, Japan would not be spewing radioactive waste into their groundwater. Moreover, the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission told Fukushima and Japan that they had a groundwater problem, and that a breach would cause widespread contamination; that if it ever melted down, it would dump nuclear waste into the ground through the water. They indicated Japan should divert the flow of the groundwater to prevent this. Still, no one died in this meltdown.
When Russia melted down a nuclear plant, it was a big mess.
When the US melted down a nuclear plant, no one was harmed and not much was released. It was just expensive to clean it.
Short version? The US is good at nuclear. Korea seems to be good at it. People shouldn't be afraid of it.
But they are. So the plants don't get financed, they don't get built, they aren't allowed to go forward.
As a result, if someone did want to finance them in the US, they would have to pay such massive interest rates that it would never pull a profit.
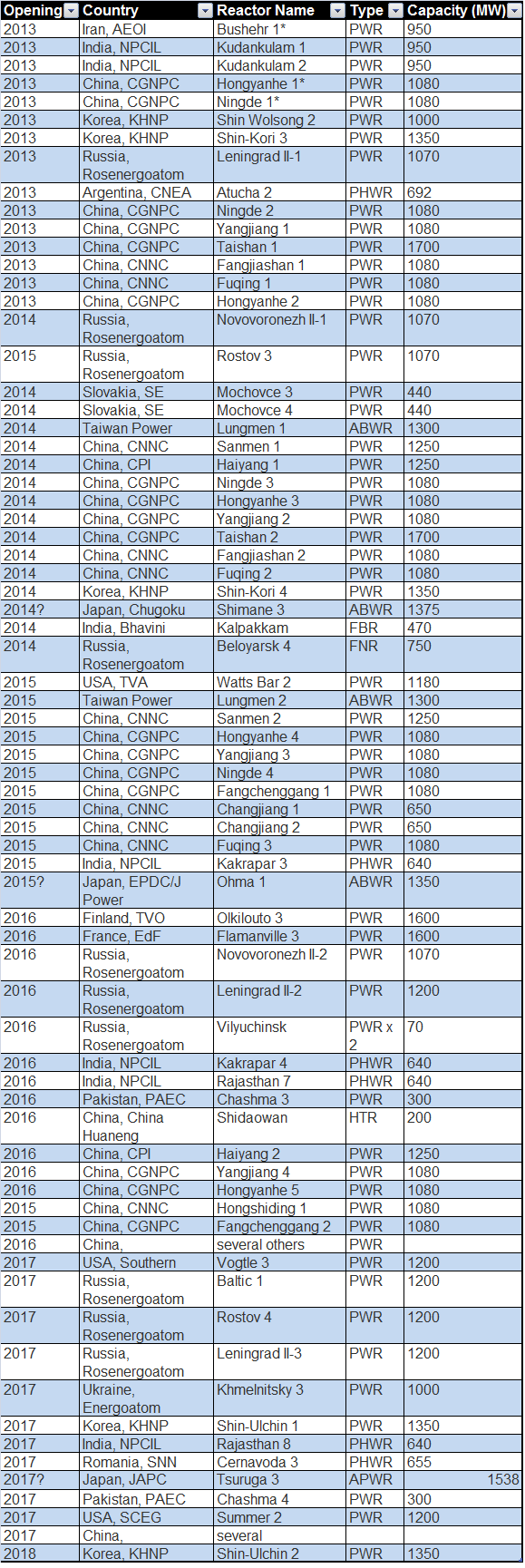
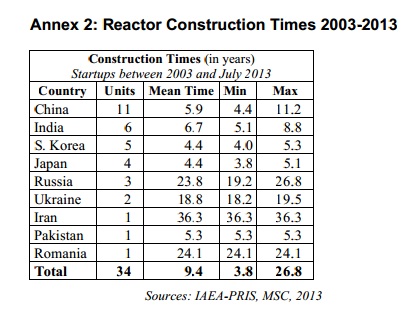
You know who is building them? Korea. China. Korea is also building power plants in the middle east. Other countries will follow suit. We need to get our house sorted out so our country can build power plants here and elsewhere, too.
Summing it Up
Live in smaller houses, it won't make you less happy. Buy less stuff, it also won't make you less happy. You also don't need to drive an SUV. Or drive as much as you do. Commuting sucks anyways.
Until all that happens, we still need a ton of electricity. Nuclear is probably the best way to do it for now.
That's my rant
Seriously. I'm pretty much done.
Thanks for reading all along. There might be a few more posts on this stuff.
- Jason Munster